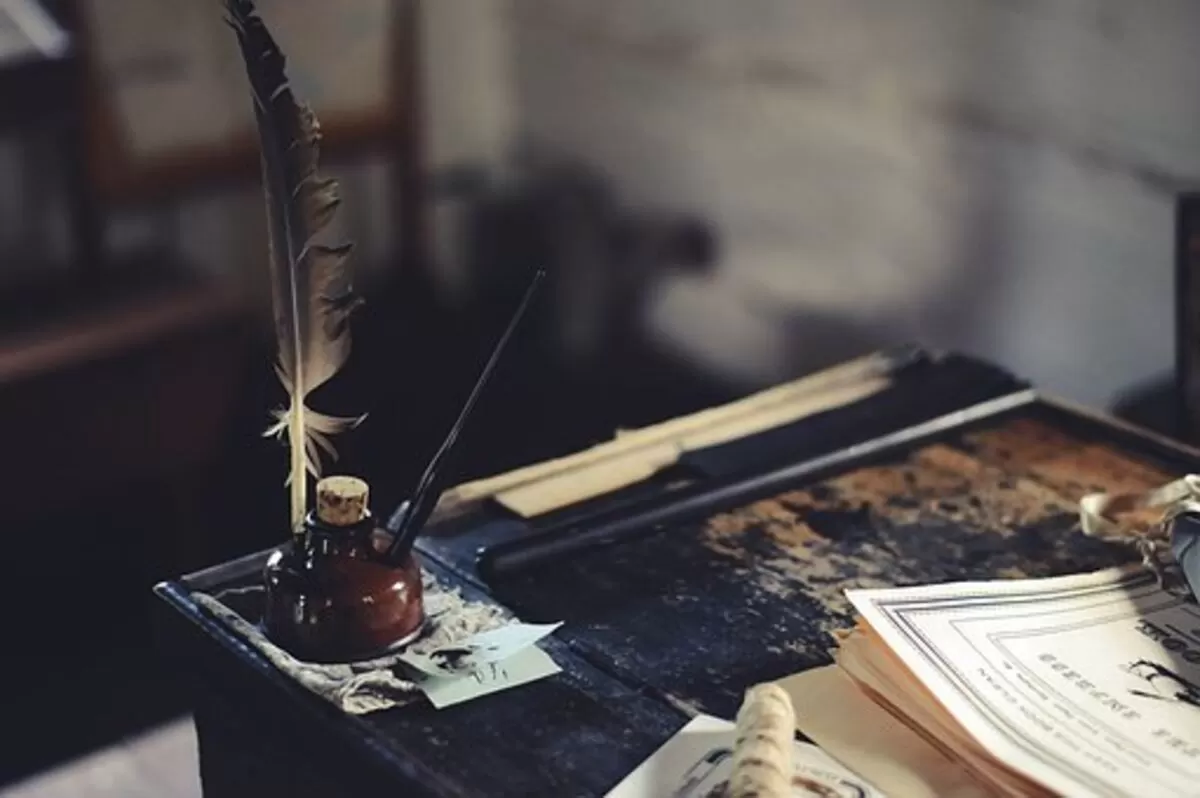

Red Blood Cells are the most plentiful type of cell in the body, and their main job is to carry oxygen to all of your cells. They also transport carbon dioxide back to the lungs. Additionally, they are vital in determining your blood type because they contain antigens that help your immune system recognize your blood type.
Red blood cells are composed of hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that binds oxygen. Red blood cells contain about 270 million hemoglobin molecules per human. Hemoglobin is enclosed within a cell membrane that comprises proteins and lipids. This membrane provides the necessary properties for physiological cell function, such as stability and deformability. Red blood cells are responsible for oxygen-carrying activities in the body and traverse the capillary network.
The oxygen-carrying function of red blood cells is mediated by hemoglobin, a pigment in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to all body parts. A complete blood cell count checks the number of red blood cells in the body and may diagnose conditions such as anemia, malnutrition, and dehydration. It can also screen for leukemia, a disease that attacks the blood’s red blood cells.
Red blood cells (RBCs) are formed by a process called erythropoiesis. This process is regulated by a hormone called erythropoietin, produced by the kidneys. It requires a variety of substances, including iron, vitamin B12, folate, and heme.
Red blood cells are the main component of the blood. These cells carry oxygen to the body’s cells and transport carbon dioxide to the lungs. RBCs make up about 0.5 million a drop of blood. Each RBC contains about 40 platelets and one WBC and is responsible for transporting oxygen.
Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the organs and tissues in our body. If you suspect that you might be hemoglobin deficient, you should have your blood checked. Hemoglobin contains four chains of amino acids that are linked to one another. One chain contains iron, and the other three contain the red pigment heme. Together, these four chains transport oxygen.
Human red blood cells are small, disk-shaped cells. They have a diameter of about 6.2 to 8.2 um, a maximum thickness of about two to three um, and a minimum thickness in the center of about 0.8 to one um. They contain around eight percent of a person’s body cells and cover nearly half of the blood.
Red Blood Corpuscles (RBC) are microscopic, disk-like cells in the blood. They do not contain a nucleus and are characterized by flexible membranes. This enables these cells to adjust their shape as they pass through the capillaries. As a result, RBCs are highly responsive to movement and increase their number in the bloodstream when people exercise or move around a lot.
The primary function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to the body’s tissues and carbon dioxide back to the lungs. The volume of blood that contains only RBCs is known as hematocrit. The RBCs contain the oxygen-carrying molecule hemoglobin, which is responsible for the red color of blood.
As the name suggests, red blood cells are nucleus-free. Their unique biconcave disk shape optimizes oxygen exchange and provides ample space for hemoglobin. Despite lacking organelles and nuclei, RBCs are still deformable and flexible. Their lack of nuclei and mitochondria also makes it challenging to synthesize RNA. However, a small number of cytoskeletal protein elements are present inside the cells.
Membrane proteins and lipids in the plasma membrane ensure cellular integrity. Studies have indicated that the lipid composition and the length of the transmembrane domains affect cellular deformability. Moreover, the presence of ion channels and water channels regulate the osmotic behavior of the cells.
The RBC complete form measures red blood cells and diagnoses anemia. A standard blood test measures the amount of hemoglobin and hematocrit in the red blood cells. It can also be used to diagnose bone marrow problems. It is always included in a complete blood count (CBC) test.
A complete blood count measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood. CBC tests are often ordered as part of routine health screening, a workup for new symptoms, or a diagnosis of a suspected condition. The results are generally expected, but a few values may be out of range. Your healthcare provider will be able to interpret the results and tell you if there is anything to worry about.
In 2017, altcoins were seen as experimental side projects to Bitcoin. By 2021, they became…
Shopping centers in Las Vegas have a unique opportunity to stand out by offering not…
Levitra, a widely recognized medication for treating erectile dysfunction (ED), has proven to be a…
Have you ever looked down at your carpet and wondered if there’s a budget-friendly way…
Counter-Strike 2 (CS2) has elevated the thrill of case openings, captivating both seasoned CS:GO veterans…
Trying to sell a car online should be simple, but sometimes buyers lose interest fast.…